AAC Plant Process – Delivering Innovation with Force Engineering
At Force Engineering, we specialize in designing and delivering fully automated AAC (Autoclaved Aerated Concrete) block manufacturing plants across India. With a strong presence in Pune, Kolhapur, and other key regions, we provide end-to-end solutions tailored to your project requirements.
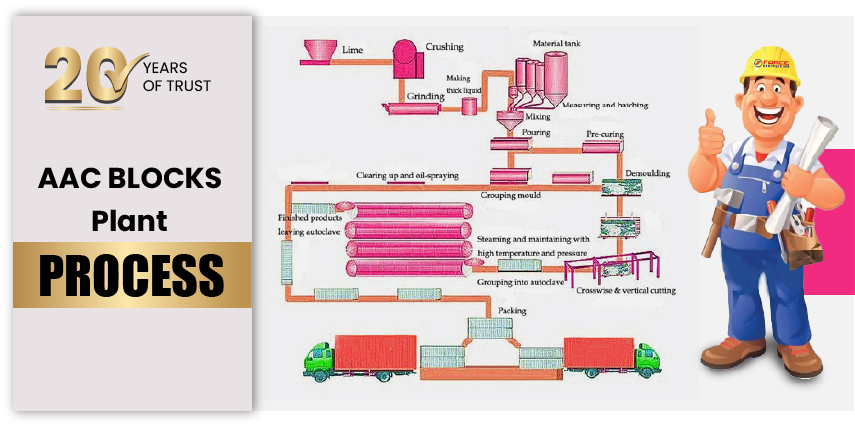
What is the AAC Plant Process?The AAC Plant Process involves the precise mixing, casting, cutting, autoclaving, and packaging of AAC blocks. These blocks are known for their lightweight properties, thermal insulation, and eco-friendliness, making them a preferred choice in modern construction
Our AAC Plant Process Includes:- Raw Material Preparation
- Mixing and Casting
- Cutting
- Autoclaving
- Final Inspection & Packaging
Lime, cement, gypsum, aluminum powder, and fly ash are carefully measured and mixed to form a homogeneous slurry.
The slurry is poured into molds where chemical reactions cause it to rise and partially set into a "green cake."
The semi-solid green cake is precision-cut into blocks using advanced cutting machines.
The cut blocks are cured in high-pressure autoclaves, enhancing strength and durability.
The finished AAC blocks undergo quality checks before being packaged and dispatched.
- Decades of Experience:
- Customized Solutions:
- After-Sales Support:
Pioneers in AAC technology with hundreds of successful installations.
Turnkey AAC plants designed to fit your production capacity and budget.
Comprehensive technical support and training provided.
Whether you're setting up a plant in Pune, Kolhapur, or anywhere in India, Force Engineering is your trusted partner. We bring unmatched expertise in executing AAC projects that meet global quality and efficiency standards.
Looking to start your own AAC block manufacturing unit?Contact Force Engineering today for a detailed consultation.
Find informative answers to all your questions about AAC Block Plant Process below.
Do you have an inquiry that's not addressed here? Please contact us via email or phone at +91 99751 42727.
The AAC block manufacturing process involves the following steps:
- Raw material preparation. The key ingredient to manufacture AAC blocks is fly ash or pond ash. ...
- Dosing and mixing. ...
- Casting, Rinsing and Pre-curing. ...
- Demoulding and cutting. ...
- Entering autoclave. ...
- Packing and loading
-Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) is a lightweight, precast, cellular concrete building material, eco-friendly, suitable for producing concrete-like blocks. It is composed of quartz sand, calcined gypsum, lime, portland cement, water and aluminium powder.
-The concrete bricks manufacturing process consists of four steps: mixing, molding, curing, and cubing. There are concrete plants which only make concrete blocks while others produce a variety of precast products like blocks, flat paver, decorative pieces like lawn edging, concrete bricks, etc.
-Unlike other bricks or concrete applications in the market, AAC is produced with no aggregate bigger than sand. As for the binding agent, the use of Quartz sand, lime (mineral), calcium gypsum, cement, and water can be seen. In addition, aluminum powder is added at a rate of 0.05% – 0.08% per unit volume.
- Stage 1. Carrying - Blocks are carried around. ...
- Stage 2. Stacking - Building Begins. ...
- Stage 3. Bridging - Lay a base block, place an upright block at both ends of it, then. ...
- Stage 4. Enclosures. - Occur soon after a child begins to use blocks regularly. ...
- Stage 5. Patterns. And. ...
- Stage 6. Early. Representation. ...
- Stage 7. Later. Representation.
- With block processing methods, a block of signal samples is being processed at a time. A block of samples is usually treated as a vector, which is transformed, to an output vector of samples by the system transformation H.
-You can use traditional or thin bed mortar. For traditional, maintain a 1:6 Cement ratio and apply at 10-15mm thickness. Thin bed mortar should be applied at about 3mm thickness.
-Maintaining the following ingredient ratios:
FLY ASH : LIME:CEMENT: GYPSUM - 69:20:8:3.
Aluminum accounts for around 0.08 percent of the total dry ingredients in the mix. Ratio of water = 0.60-0.65.
-Special quicklime is used in aerated autoclaved concrete (AAC) mixes, in order to maximize the efficiency of each factory. It foams after reacting with ingredients to form tobermorite, resulting in an insulating low-carbon solution for masonry construction.
-The process involves cleaning and inspecting the block, boring and honing the cylinders, surfacing the deck, and align honing or align boring the main bearing bores, among other operations. Each machining step is crucial in achieving precise tolerances and surface finishes.
-AAC blocks are made from a mixture of sand, cement, lime, gypsum, water, and an aerating agent. The aerating agent is typically aluminium powder or paste, which reacts with the other ingredients to release hydrogen gas. This gas expands and forms bubbles within the mixture, resulting in a foam-like substance.